What do PDUs do?
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is a critical component in data centers, server rooms, and other environments where multiple devices require power. Essentially, a PDU acts as an intermediary between the main power source and the IT equipment, ensuring that electricity is distributed efficiently and safely. The primary function of a Power Distribution Unit is to take power from a utility source or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and deliver it to servers, networking equipment, and other devices within a rack.
In a typical data center setup, a Power Distribution Unit is installed in a standard rack, providing multiple outlets that can accommodate various types of plugs. This allows IT administrators to power multiple devices from a single source, simplifying the wiring and reducing the risk of overloading circuits. Additionally, PDUs often include features such as circuit breakers, which protect against overcurrent and potential fire hazards.
One of the key benefits of using a Power Distribution Unit is its ability to centralize power management. Instead of running individual power cords from each device to the main power source, a PDU consolidates these connections, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot. This centralization also improves safety by reducing the number of exposed power cords and minimizing the risk of accidental disconnections.
Moreover, PDUs can be equipped with surge protection, which safeguards sensitive IT equipment from voltage spikes and other electrical disturbances. This is particularly important in environments where power quality may be inconsistent, as it helps to prevent data loss and hardware damage. Some advanced PDUs also offer remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing administrators to manage power usage and troubleshoot issues from a central location.
How do PDUs work?
The operation of a Power Distribution Unit is relatively straightforward but highly effective. At its core, a PDU takes power from a single input source and distributes it to multiple output outlets. The input source can be either a standard utility power supply or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS), depending on the specific requirements of the environment.
When power enters the PDU, it passes through a main circuit breaker, which serves as a safety mechanism to prevent overcurrent. From there, the power is routed to various internal components, such as surge protection circuits and voltage regulation systems, before being distributed to the outlets. Each outlet on the PDU is designed to accommodate specific types of plugs, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of IT equipment.
In basic PDUs, the power distribution process is passive, meaning that once the power is connected, it is simply passed through to the outlets without any additional control or monitoring. These PDUs are often referred to as “dumb” PDUs because they lack any form of intelligence or remote management capabilities.
On the other hand, intelligent PDUs incorporate advanced features that allow for greater control and monitoring. These PDUs are equipped with sensors that measure various power parameters, such as voltage, current, and power consumption. This data is then transmitted to a central management system, where administrators can monitor the power usage of individual devices and make adjustments as needed.
Intelligent PDUs also offer remote control capabilities, allowing administrators to turn outlets on or off, reset devices, and even schedule power cycles. This level of control is particularly useful in data centers, where IT equipment may need to be managed remotely or during off-hours. Additionally, intelligent PDUs can integrate with other management systems, such as environmental monitoring and asset management tools, providing a comprehensive view of the data center’s operational status.
Another important aspect of how PDUs work is their ability to handle different power loads. PDUs are designed to support a specific maximum current, and it is crucial to ensure that the total power draw of the connected devices does not exceed this limit. Overloading a PDU can lead to tripped circuit breakers, power outages, and potential damage to equipment. Therefore, careful planning and load balancing are essential when deploying PDUs in a data center or server room.
What are the different types of PDU form factors?
Power Distribution Units come in various form factors, each designed to meet specific installation and operational requirements. Understanding these different form factors is essential for selecting the right PDU for a particular environment. The most common form factors include rack-mount PDUs, floor-standing PDUs, and wall-mounted PDUs.
Rack-mount PDUs are the most widely used form factor in data centers and server rooms. These PDUs are designed to be installed in standard 19-inch racks, which are the industry standard for housing IT equipment. Rack-mount PDUs come in various sizes, typically ranging from 1U to 4U in height, where 1U equals 1.75 inches. This modular design allows for flexible deployment, as multiple PDUs can be stacked within a rack to accommodate different power requirements.
Floor-standing PDUs, also known as tower PDUs, are standalone units that are placed on the floor. These PDUs are often used in environments where rack space is limited or when a higher power capacity is needed. Floor-standing PDUs can support a greater number of outlets and higher current loads compared to rack-mount PDUs, making them suitable for larger data centers or facilities with high power demands.
Wall-mounted PDUs are designed to be mounted directly onto a wall, making them ideal for smaller server rooms or environments where space is at a premium. These PDUs are typically less powerful than rack-mount or floor-standing PDUs but offer a convenient solution for distributing power to a limited number of devices. Wall-mounted PDUs are also easier to access for maintenance and troubleshooting, as they are not enclosed within a rack.
In addition to these primary form factors, PDUs can also be classified based on their input and output configurations. For example, some PDUs are designed to accept three-phase power, which is commonly used in large data centers, while others are optimized for single-phase power, which is more typical in smaller environments. The number and type of outlets on a PDU can also vary, with options ranging from standard NEMA plugs to specialized IEC connectors.
Another consideration is the environmental conditions in which the PDU will operate. Some PDUs are built to withstand harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or dust, and are therefore suitable for outdoor or industrial applications. These PDUs often come with additional features, such as weatherproof enclosures and enhanced cooling systems, to ensure reliable operation in challenging environments.
Challenges of using PDUs
Implementing Power Distribution Units (PDUs) in data centers and server rooms, while beneficial, comes with several challenges. Key issues include managing the increasing power demands of modern IT equipment to prevent overloading, integrating PDUs seamlessly with other data center management systems like UPS and monitoring tools, and ensuring the security of networked, intelligent PDUs against cyber threats. Maintenance, troubleshooting, and the higher costs associated with advanced PDUs also pose significant hurdles, alongside the need to keep pace with rapidly evolving technology.
Choosing the right PDU
Selecting the appropriate PDU requires careful consideration of several factors. It’s crucial to match the PDU’s power capacity and specifications to the environment’s needs, choose the correct form factor (rack-mount, floor-standing, or wall-mounted) based on space and layout, and decide between basic or intelligent models based on required monitoring and control features. Integration compatibility with existing management systems, budget constraints including total cost of ownership, and the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability and support are also vital considerations in making the right choice.
Installing a PDU
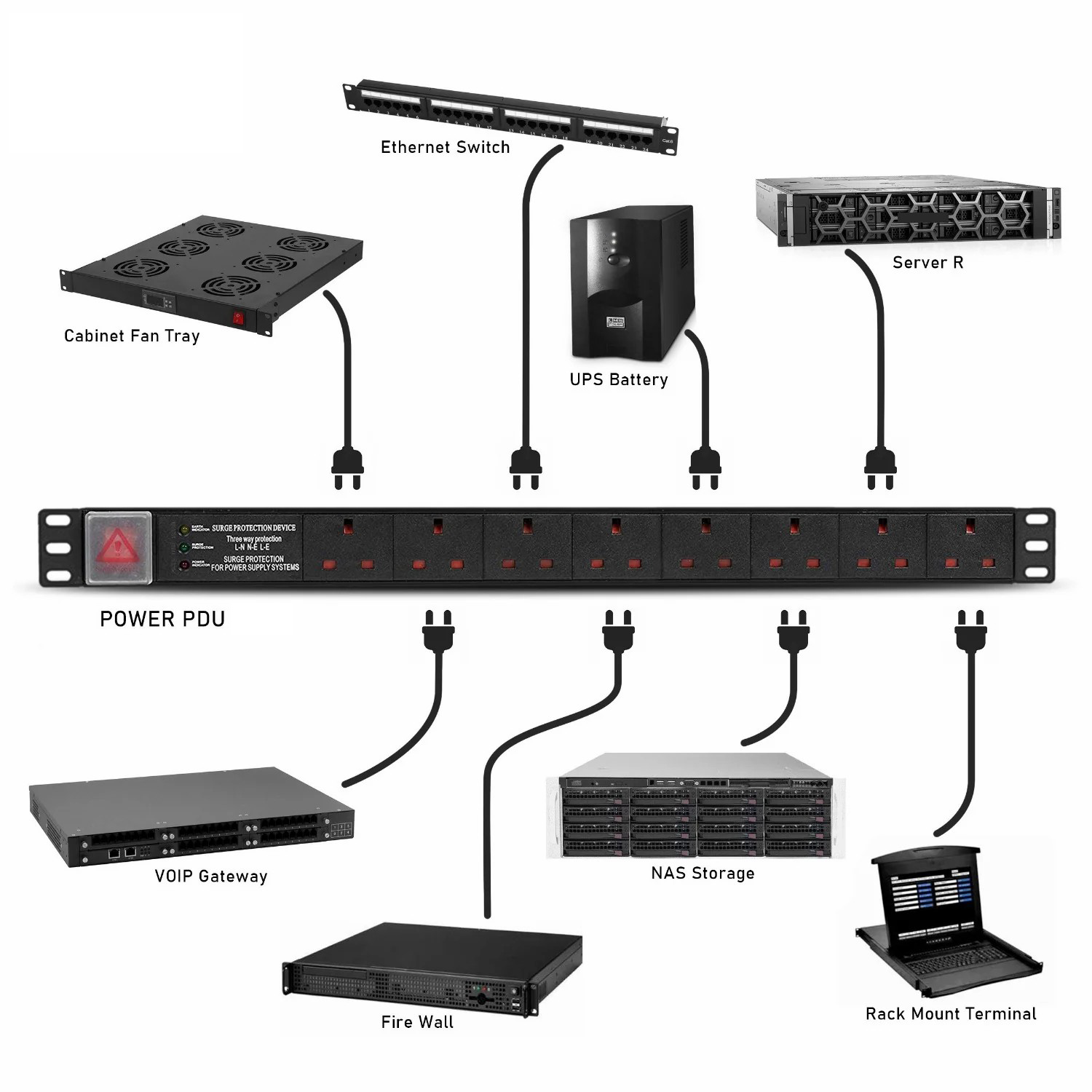
Installing a PDU correctly is fundamental for reliable operation. The process involves meticulous planning for placement to ensure accessibility and proper airflow, thorough site preparation including ensuring a clean and properly grounded area, and secure mounting according to the PDU type and manufacturer guidelines. Careful connection of the input power source and the output devices, followed by rigorous testing to confirm correct voltage, current, and functionality (including configuration for intelligent PDUs), ensures the PDU operates safely and effectively. Proper installation minimizes risks like overloading and equipment damage, supporting the efficient operation of IT equipment.
FAQ
F: What is the function of power distribution unit?
Q: A power distribution unit (PDU) is a device with multiple power outlets that provides electrical protection and distributes power to IT equipment within a rack. PDUs can either be basic (also known as “dumb”) or intelligent, and there are multiple types of intelligent rack PDUs.
F: Why do I need a PDU?
Q: A PDU, or power distribution unit, is a device with multiple outlets. It is designed to be installed in a standard rack, where its main function is to distribute reliable network power from utility power source or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to multiple devices.

















